RAK ICC IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland UAE (2026)
Recent Insights

Table of Contents
Introduction
In the current UAE business environment, the “one-size-fits-all” approach to company formation is dead. Founders and international investors are now faced with a tripartite choice: RAK ICC IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland. Each serves a distinct strategic purpose, and choosing the wrong one can lead to frozen bank accounts, tax non-compliance, or the inability to sponsor staff.
This guide provides an exhaustive analysis of these three pillars of the UAE corporate structure. We will explore the fundamental differences between holding assets and operating a business, the reality of RAK ICC vs Free Zone banking, and why the RAK ICC vs Mainland debate usually comes down to where your customers are located.
By the end of this deep dive, you will understand the nuances of the RAK ICC Free Zone vs Mainland comparison, including a 2026 cost breakdown, a functional decision tree, and the “Hybrid Model” currently being deployed by family offices and tech founders to ring-fence assets while maintaining operational flexibility.
Quick Summary
- Best for Asset Holding: RAK ICC IBC offers the most robust framework for international asset holding and succession planning without the overhead of a physical office.
- Best for International Services: Free Zone entities provide a middle ground, offering 100% ownership and UAE residency visas with a “mid-shore” reputation.
- Best Local Trade: Mainland companies are essential if your primary revenue comes from the UAE domestic market or government contracts.
- The Gold Standard: A hybrid model using an RAK ICC holding company to own a Free Zone operating subsidiary is the preferred structure for sophisticated investors in 2026.
Which Should You Choose?
The decision-making process for RAK ICC IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland generally follows the nature of your “economic nexus” to the UAE.
When to use RAK ICC IBC
You should opt for a RAK ICC company setup if your primary objective is international asset holding, protecting intellectual property, or creating a private trust/foundation structure. It is an offshore vehicle, meaning it is “non-resident” for most operational purposes in the UAE but is governed by world-class common law-style regulations.
When to use Free Zone
A Free Zone is the go-to for “mid-shore” operations. It is the right choice if you require UAE residency visas, a physical office (or flexi-desk), and plan to provide services globally or to other Free Zone companies. It offers Mainland vs Free Zone ownership parity (100% foreign ownership) but with a more streamlined regulatory environment for specific industries like tech, media, or consulting.
When to use Mainland
A Mainland company’s setup process is mandatory if you intend to trade directly with the UAE retail market, provide services to local government entities, or operate in regulated sectors like real estate brokerage or large-scale construction. Mainland vs Free Zone company benefits Centre largely on the “onshore” nature of the license, allowing you to bid for any contract within the Emirates.
The Common Best Option: The Hybrid Model
For many of our clients, the answer isn’t one or the other. We frequently implement a RAK ICC Holding Company that owns 100% of a UAE Free Zone Operating Company. This provides the ultimate layer of protection, separating the assets (held in the IBC) from the operational risks and liabilities (in the Free Zone).
What Each Structure Really Is
To understand the RAK ICC vs Free Zone UAE landscape, we must define the legal DNA of these entities.
What is a RAK ICC IBC?
Ras Al Khaimah International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC) is a first-class international corporate registry. These offshore corporations are registered as International Business Companies (IBCs).
It cannot trade within the UAE Mainland and cannot lease physical office space in the country (it uses a registered agent’s address). However, RAK ICC company ownership is highly flexible, allowing for various share classes and integration with RAK ICC Foundations for succession planning.
Case Study: The IP Fortress
A European software firm wanted to centralise its global IP while expanding into Asia. DBTA implemented an RAK ICC structure to hold the patents, licensing them back to operational subsidiaries. This protected the IP from the liabilities of the trading arms.
RAK ICC
IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland UAE (2026)
Watch this short video to see how IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland UAE (2026) explained simply in under 60 Second.

What is a Free Zone company?
A Free Zone company is a “bounded” onshore entity. Each Free Zone (such as DMCC, DIFC, or Shams) acts as its own regulatory ecosystem. While these companies are physically located in the UAE, they are technically outside the UAE customs territory for goods. They are excellent for Free Zone vs Mainland flexibility, as they offer 100% foreign ownership and easier recruitment processes for expatriate talent.
Case Study: The Global Digital Agency
A digital agency with a remote team of 20 needed a hub. DBTA guided them through a Free Zone vs Mainland UAE Company analysis, choosing a Sharjah-based Free Zone to optimise costs while securing visas for the core leadership team.
What is a Mainland company?
This refers to any onshore entity licensed by the Department of Economy and Tourism (DET) in an Emirate such as Dubai or Abu Dhabi. In the past, you would have needed a local partner (Emirati National) to be the 51% owner; recent reforms mean that Mainland vs Free Zone ownership is mostly a level playing field and now typically 100% foreign owned for most commercial/industrial activities.
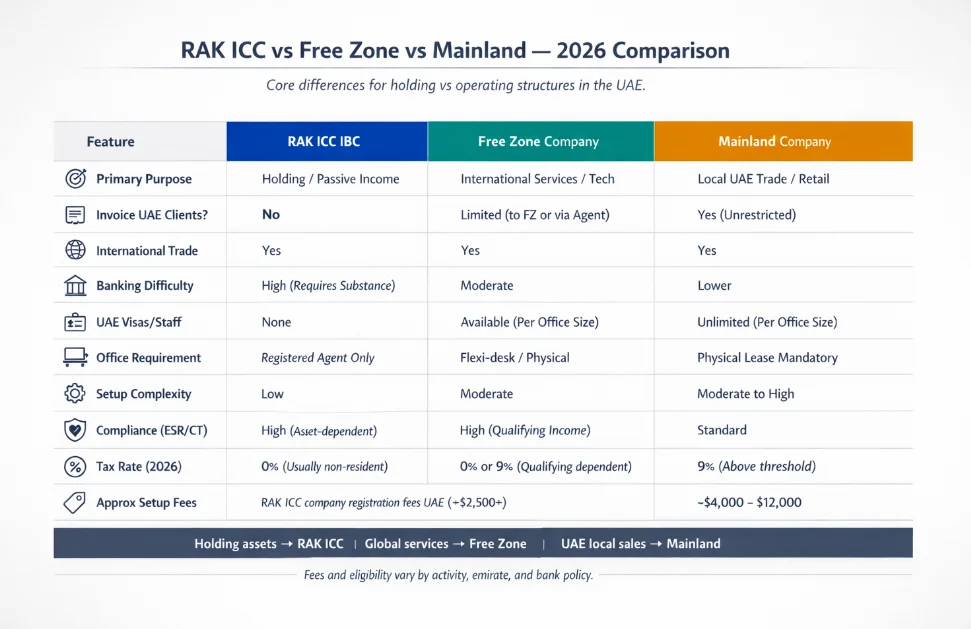
2026 Comparison Table (Core Section)
The following table highlights the critical distinctions in the RAK ICC vs Free Zone vs Mainland debate, updated for the 2026 regulatory environment.
| Feature | RAK ICC IBC | Free Zone Company | Mainland Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Holding / Passive Income | International Services / Tech | Local UAE Trade / Retail |
| Invoice UAE Clients? | No | Limited (to FZ or via Agent) | Yes (Unrestricted) |
| International Trade | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Banking Difficulty | High (Requires Substance) | Moderate | Lower |
| UAE Visas / Staff | None | Available (Per Office Size) | Unlimited (Per Office Size) |
| Office Requirement | Registered Agent Only | Flexi-desk / Physical | Physical Lease Mandatory |
| Setup Complexity | Low | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Compliance (ESR / CT) | High (Asset-dependent) | High (Qualifying Income) | Standard |
| Tax Rate (2026) | 0% (Usually non-resident) | 0% or 9% (Qualifying dependent) | 9% (Above threshold) |
| Approx Setup Fees | RAK ICC company registration fees UAE (~$2,500+) | ~$4,000 – $12,000 | ~$5,000 – $15,000+ |
Post-2025 / 2026 Tax Reality

The UAE tax landscape changed forever on 1 June 2023, and by 2026, the “settled” reality of Corporate Tax (CT) is a primary driver in the RAK ICC vs Free Zone tax rates discussion.
The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) now oversees a 9% corporate tax on taxable income exceeding AED 375,000. However, the nuances are where complexity lies. In the context of RAK ICC vs Free Zone tax exemption, many investors incorrectly assume an IBC is automatically exempted.
If an RAK ICC IBC is managed and controlled within the UAE, it may be considered a tax resident. Conversely, a Free Zone entity may qualify for a “0% Qualifying Free Zone Person” status if it maintains adequate substance and earns “Qualifying Income.” RAK ICC tax treatment is now strictly tied to Tax Residency status, the nature of the income (passive vs. active), and the location of Effective Management and Control.
Before committing to a RAK ICC vs Free Zone structure, you must verify your “Qualifying Income” status. Relying on outdated “tax-free” marketing is the quickest way to face a post-audit penalty from the FTA.
Case Study: Navigating the 9%
A trading company in DMCC was worried about losing its tax-free status. DBTA conducted a tax audit and restructured its inter-company agreements to ensure their income remained “Qualifying” under the new 2026 guidelines.
Banking Reality
The single biggest friction point in RAK ICC vs Mainland compliance is banking. Opening a corporate bank account in the UAE in 2026 requires more than just a business licence; it requires a “Business Profile” that passes stringent KYC and EDD (Enhanced Due Diligence).
- Offshore (RAK ICC): Banks view these as “high risk” because they lack physical substance in the UAE. Unless the IBC is a holding company for a larger, cash-flow-positive group or holds significant real estate, opening up a local account is challenging.
- Free Zone: This is the standard. Banks are comfortable with Free Zone entities provided there is a clear “Source of Wealth” (SoW) and a legitimate business plan.
- Mainland: Often the “gold child” for banks. Because a Mainland company requires a physical lease verified by Ejari, banks see this as a high-commitment, low-risk structure.
Why does the structure affect approval:
Banks are under pressure to prevent “shell companies.” A RAK ICC vs Free Zone UAE comparison from a banker’s perspective always looks at whether you have a desk, a phone line, and a resident manager.
If you have none of these, your RAK ICC company setup may require an international bank account (e.g., in Mauritius or Switzerland) rather than a local one in Dubai.
Hybrid Model (RAK ICC + Free Zone)
The “Hybrid Model” is the sophisticated answer to the RAK ICC vsFree Zone vs Mainland dilemma.
The Structure:
1. Top Co: A RAK ICC IBC acts as the parent holding company. It holds the IP, the retained earnings, and the shares of the operating entities.
- Op Co: A UAE Free Zone company is owned 100% by the RAK ICC IBC. This entity hires staff, leases an office, and interacts with clients.
Why use it? This provides the RAK ICC benefits of easy share transfers and succession planning (often using a RAK ICC Common Law Foundation). In contrast, the Free Zone entity provides the “substance” and visa eligibility required for UAE residency and banking.
When not using it: If you are a solo consultant with a low turnover, the RAK ICC vs Free Zone setup timeline and the double renewal fees (holding + operating) may not justify the cost. This is for businesses scaling toward an exit or those managing significant family wealth.
Decision Tree
To simplify your choice between RAK ICC IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland, follow this logical path:
Do you need to trade with UAE retail customers?
* Yes → Mainland
Do you need a UAE residency visa?
Yes → Free Zone
No → Proceed to 3
Are you only holding assets (Property, IP, Shares)?
Yes → RAK ICC IBC
Are you separating high-value assets from daily business risks?
Yes → Hybrid (RAK ICC + Free Zone)
Still unsure where your business fits? DBTA provides a complimentary 15-minute structuring audit. Book your session here.
Common Mistakes

Through years of practice, we see the same “structuring traps” repeatedly. Avoiding these is critical for RAK ICC vs Mainland compliance.
- Using offshore when you need an operating licence: Attempting to run a consultancy from an RAK ICC IBC to save on costs. You will eventually be caught when a client asks for a Tax Residency Certificate or a VAT TRN, neither of which is easily obtainable for offshore entities.
- Using Free Zone for holding only: While possible, the renewal fees for a Free Zone are much higher than the RAK ICC cost 2026 rates. If you don’t need visas, don’t pay for a Free Zone.
- Assuming Mainland fixes banking: A Mainland licence without a real office or a credible manager will still be rejected by banks.
- Activity vs Transaction Mismatch: Getting a “General Trading” licence but only doing “Investment Holding.” This triggers Red Flags during annual AML reviews.
- Starting setup before banking strategy: Never pay for a licence until you have vetted your business model with a banking consultant.
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario A: The Investor / Holding Group
An international investor wants to hold a portfolio of Dubai apartments and shares in European startups.
- Recommendation: RAK ICC IBC.
- Why: Low maintenance, high privacy, and RAK ICC benefits regarding the UAE’s “will and probate” laws.
Scenario B: E-commerce or Services Company
A tech founder moving to Dubai to run a global SaaS platform.
- Recommendation: Free Zone (e.g., IFZA or DMCC).
- Why: Free Zone vs Mainland UAE logic applies here, no need for local retail access, but 100% need for visas and a “mid-shore” banking profile.
Scenario C: UAE Expansion with Holding Structure
A UK business expanding to open physical coffee shops in Dubai.
- Recommendation: RAK ICC IBC (Holding) owning a Mainland LLC (Operating).
- Why: The RAK ICC vs Mainland combination ensures that the UK parent company’s liability is limited, while the Mainland entity has the legal right to lease retail space in malls.
How DBTA Helps
At Dubai Business and Tax Advisors, we don’t just “sell licences.” We design corporate architectures that survive the scrutiny of banks and tax authorities. Our implementation process includes:
- Eligibility and Activity Assessment: We map your business model against the 2,000+ available UAE activities to ensure you aren’t under-licensed or over-paying.
- Structure Recommendation: A bespoke report on RAK ICC vs Free Zone vs Mainland suitability based on your 5-year growth plan.
- Bank-Ready KYC / SoF / SoW Pack: We prepare the professional dossier that banks actually want to see, significantly reducing the risk of rejection.
- Hybrid Ownership Setup: Professional execution of the RAK ICC Holding / Free Zone Operating model.
- Compliance and Renewal Management: We act as your outsourced corporate secretary, ensuring ESR filings, UBO registers, and licence renewals are handled on time.
Case Study: The Exit Strategy
A tech startup was preparing for a Series A. Dubai Business & Tax Advisors team restructured its messy Mainland setup into a clean RAK ICC Holding model, making the due diligence process simple for international investors.

Conclusion
The choice between RAK ICC IBC vs Free Zone vs Mainland is the foundation upon which your UAE success is built. In 2026, the stakes are higher than ever. An IBC is a powerful tool for protection; a Free Zone is an engine for international growth, and a Mainland company is your gateway to the local economy.
For most high-net-worth individuals and scaling startups, the “Hybrid Model” is the superior choice, offering the best of both worlds. However, the nuances of your specific “Source of Wealth” and “Qualifying Income” must be the final arbiters of your decision.
FAQ's:
The real difference is in their operational geography. RAK ICC is offshore (non-resident), Free Zone is “mid-shore” (within a zone) and Mainland onshore (anywhere in the UAE).
In only the base RAK ICC cost 2026 terms, the IBC is the cheapest. Yet, when you consider visa costs and office rentals, for service-based businesses, Free Zone (even though a bit pricier) ends up being cheaper than Mainland.
Not necessarily. Under the 2026 rules, RAK ICC vs Free Zone tax exemption depends on “Qualifying Income” and “Substance.” All three can hit a 0% rate if they meet specific FTA criteria.
Yes. Mainland vs Free Zone ownership restrictions have been largely removed and RAK ICC company ownership has always allowed 100% foreign control.
RAK ICC company registration costs in the UAE are AED 8,000 – 10,000. The Free Zones have between AED 15,000 and AED 50,000. Mainland relies on the activity and the Emirate, but from AED 18,000.
They all have a Shareholder and UBO Register. At Free Zone and the Mainland, they must go through an audit annually (mostly your). With RAK ICC vs Mainland compliance for IBCs, the question is whether they are doing Relevant Activities in respect of Economic Substance Regulations.
The RAK ICC vs Free Zone setup timeline is fast (3–5 days). Mainland can take 1–2 weeks, depending on the need for external approvals (e.g., KHDA or DHA).
Renewals are generally 80-90% of the initial setup cost.
Yes, but the RAK ICC vs Free Zone pros and cons for international trade often come down to whether your supplier/customer requires you to be on a “Whitelist” of resident tax entities.
RAK ICC IBC provides zero visas. Free Zone and Mainland provide visas based on the square footage of the office leased.
Free Zone vs Mainland flexibility favours Mainland for geographic reach, but Free Zone for administrative ease.
Only in highly sensitive sectors (Defence, Oil & Gas), where Mainland entities may still require local majority ownership.
Yes, all three support multiple shareholders and corporate shareholders.
The hybrid model (RAK ICC holding a Free Zone or Mainland entity) is best for scaling.
Latest news & articles

LLC Trade License Cost in Dubai (2026): Full Breakdown of Fees, Approvals, and Renewal Charges
Read More »
Living Expenses in Dubai (2026): Real Monthly Budgets for Singles, Couples, and Families
Read More »
UID Number in the UAE: How to Find It, Where It Appears, and Why It Matters for Visas and Emirates ID
Read More »About the Author:
AURANGZAIB CHAWLA
As CEO of DBTA, Aurangzaib Chawla advises globally mobile businesses and individuals on cross-border tax planning and structuring. With expertise spanning the UK, UAE, and wider GCC, Zaib helps clients minimise double taxation, protect assets, and achieve long-term financial efficiency while staying fully compliant.
Planning to launch in Dubai or the UAE?
Let’s talk about how to structure your business for growth the smart, compliant, and tax-efficient way
About the Author:
AURANGZAIB CHAWLA

As CEO of DBTA, Aurangzaib Chawla advises globally mobile businesses
and individuals on cross-border tax planning and structuring. With expertise spanning the UK, UAE, and wider GCC, Zaib helps clients minimise double taxation, protect assets, and achieve long-term financial efficiency while staying fully compliant.
Planning to launch in Dubai or the UAE?
Let’s talk about how to structure your business for growth the smart, compliant, and tax-efficient way.